Citations are the backbone of scientific publishing, connecting ideas across time and space. They enable research performed in a lab in 2021 in New York to build upon a discovery from 1889 in a West London Hospital. They can be used to support a new line of research or to question the status quo. They help readers verify the claims authors make and they are also a proxy of research impact.
Citations are central to scientific discovery and yet they are used pretty superficially, mostly as a simple number without any contextual meaning. Sayings such as, “this paper has been cited 100 times” or “they are a highly cited author” are all too common amongst researchers. But what do they actually mean? What do those 100 citations say about the research besides that it has been mentioned in 100 other papers? Has the work been verified or disproven by other studies?
Scite, Copyright Clearance Center’s newest partner, makes these questions easy to answer and make citations useful beyond just a superficial number through “Smart Citations.”
Here’s a look at how they work, and how they can be beneficial across the R&D pipeline.
What are Smart Citations?
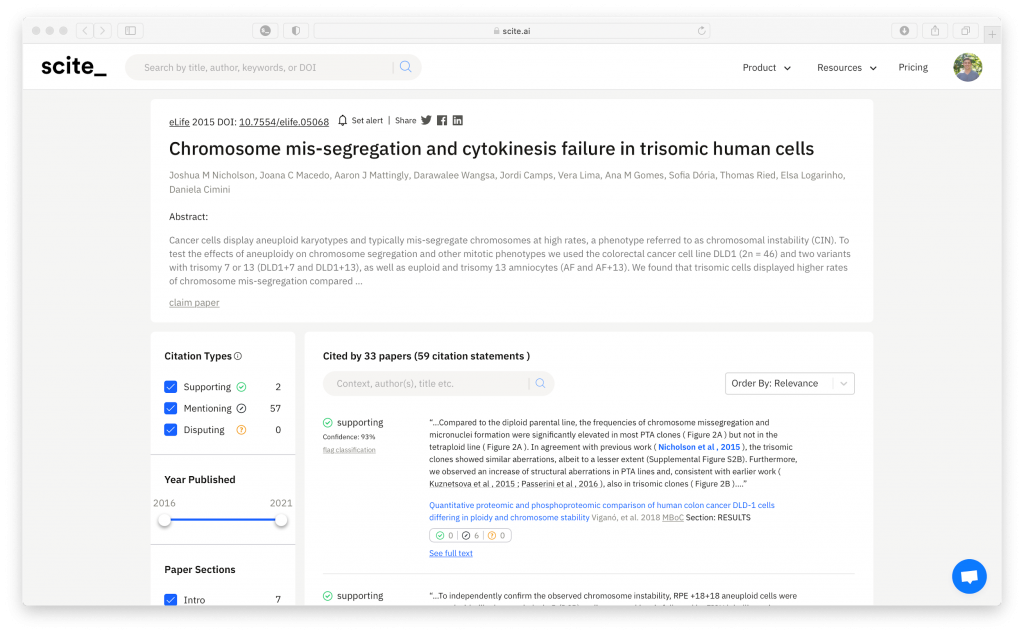
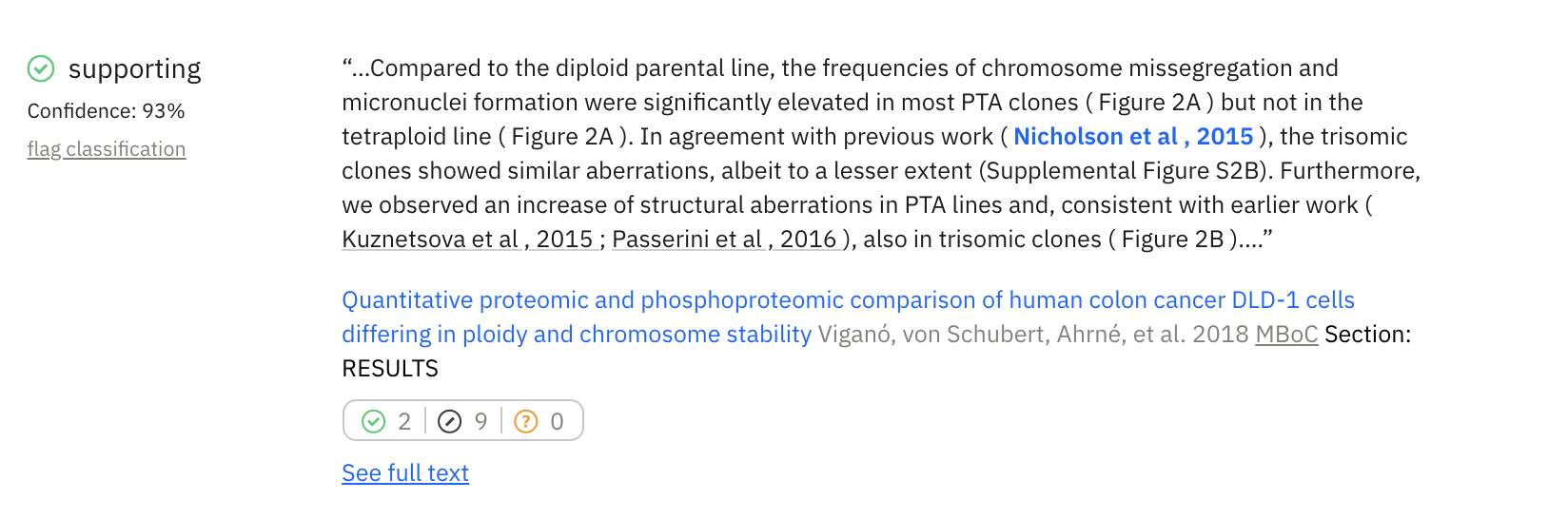
Smart Citations are just like normal citations, but they add a rich source of information beyond the typical metadata to metadata linkage. First and foremost, Smart Citations show the context of the citation by showing the sentence where the citation was used in the citing paper.
For example, my PhD work (Nicholson et. al, 2015) has been cited 48 times. Looking at a traditional citation index will allow you to see a list of papers citing my work, but they don’t make it easy to see what each of those citing articles say about research. With Smart Citations, you can immediately see the citation statement, where it was made in the citing paper (e.g. introduction versus results section etc.), and if it provides supporting or contrasting evidence.
This allows anyone to look at any piece of research and see how it has been cited. In addition to the citation context, this approach offers various ways to filter and search the citations. To help identify reliable research, you can select for “supporting” or “contrasting” citations. These citations have been classified by a deep learning model that automatically identifies if a citation provides supporting or contrasting evidence. With this you can see that my work has been supported by subsequent research almost immediately.
How are Smart Citations made?
To create Smart Citations, full-text scientific articles are processed to extract and analyze citation statements. This requires substantial computational power to identify in-text citations, match them to the reference in the reference list, and match that against a database of publications. scite utilizes over 11 machine learning models to extract and match citations from PDFs, the most commonly used filetype of scientific publications. To-date, scite has processed over 24M scientific articles, extracting and analyzing over 800M citation statements across nearly all disciplines.
Once citation statements have been matched to their citing article and extracted from the full-text of the scientific publication, they are classified using a Deep Learning model. The Deep Learning model has been trained on roughly 50,000 expert-annotated citation statements, taking into account the rhetorical function of the sentence, not just positive or negative sentiment.
How can Smart Citations help me?
Smart Citations unlock a wealth of information from scientific articles and make it easy to digest and understand. Historically, most researchers have not looked at what every citation a paper they are reading says because it would be simply too much work and near impossible in some cases. With Smart Citations, you can easily see this information and better understand how an article or multiple articles fit within the literature landscape.
CCC is excited to announce the integration of the Free version of scite Smart Citations software within RightFind Navigate, with separately purchasable upgrades to Premium and Enterprise versions of scite Smart Citations software available directly via scite.ai. Contact CCC here to learn more.